Event Overview
- Date: March 13 (Thu) - March 14 (Fri), 2025
- Official link: https://aws.amazon.com/jp/blogs/news/aws-jumpstart-2025/
Day 1 Morning
System for the Prototype Phase (Under 100 Users)
graph TD
User -- Request--> Route53
Route53 -- DNS Resolution --> ElasticIP
subgraph VPC [AWS VPC]
ElasticIP --> EC2
EC2 -->| RDS
RDS -->| EC2
EC2 --> ElasticIP
end
Key Components:
- Route 53: AWS DNS service. Responsible for converting domain names to IP addresses.
- Elastic IP: A service providing static IP addresses. Allows EC2 instances to maintain the same IP address after restarts.
- EC2: A service providing virtual server instances. Runs applications.
- RDS: Relational Database Service. Handles data persistence.
Characteristics of this phase:
- Simple architecture enabling rapid development and deployment
- Can be operated with minimal resources
- Single points of failure exist, limiting high availability
- No horizontal scaling mechanism
About VPC
What is VPC?
VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) is a service for creating your own virtual network on AWS. It provides the same level of control as an on-premises network environment, allowing fine-grained management of security and network settings.
Subnet Concepts
- Subnet: A unit that partitions IP address ranges within a VPC
- Public Subnet: A subnet with direct internet access
- Private Subnet: A subnet not directly accessible from the internet
Security Controls in VPC
NACL (Network Access Control List):
- Subnet-level security control
- Stateless (inbound and outbound traffic must each be configured separately)
- Both allow and deny rules can be set
- Numbered rule list for priority management
Security Group:
- Instance-level security control
- Stateful (allowing inbound traffic automatically allows return traffic)
- Only allow rules can be set (no explicit deny)
- Easy to allow communication between instances in the same security group
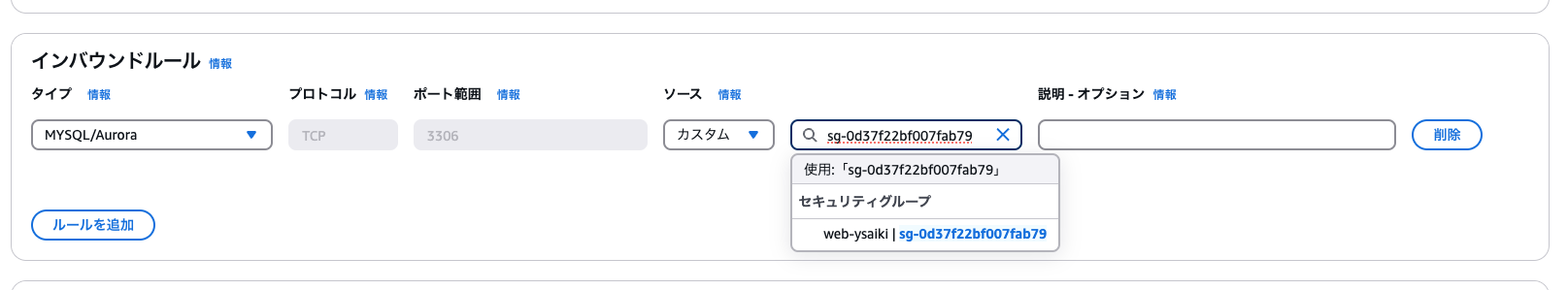 A security group can be specified as an inbound source
A security group can be specified as an inbound source
VPC Endpoints
VPC endpoints allow connections to AWS services (S3, DynamoDB, etc.) without going through an internet gateway or NAT gateway. This keeps traffic within the AWS network, improving security.
- Gateway Endpoint: Used for access to S3 and DynamoDB
- Interface Endpoint: Used for access to other AWS services
About EC2
Basic EC2 Instance Concepts
- AMI (Amazon Machine Image): A template containing the configuration information for an EC2 instance
- Instance Type: A combination of CPU, memory, storage, and network performance
- EBS (Elastic Block Store): Persistent storage volumes attachable to EC2 instances
Choosing an Instance Type
Selecting the appropriate instance type based on the use case is important:
- General Purpose (T3, M5, etc.): Balanced compute, memory, and network performance
- Compute Optimized (C5, etc.): Workloads requiring high-performance CPUs
- Memory Optimized (R5, etc.): Applications processing large datasets
- Storage Optimized (I3, D2, etc.): Workloads requiring high I/O performance
- Accelerated Computing (P3, G4, etc.): Machine learning and graphics processing using GPUs
Managing EC2 Instances
- Launch: Create and start an instance
- Stop: Shut down an instance (data is retained)
- Reboot: Restart an instance
- Terminate: Permanently delete an instance (data is deleted)
Using Session Manager
AWS Systems Manager Session Manager allows you to securely connect to EC2 instances without opening inbound ports.
Benefits:
- No need to open SSH port (22)
- No key pair management required
- Connection logs can be recorded in CloudTrail and CloudWatch Logs
- IAM policies can be used for connection authentication
Day 1 Morning
System for the 10,000-User Phase
As the number of users increases, a single EC2 instance can no longer handle the load. A more robust architecture is needed.
graph TD;
User -- Request --> Route53;
Route53 -- DNS Resolution --> ALB;
subgraph VPC
ALB -- Load Balance --> EC2_1
ALB -- Load Balance --> EC2_2
subgraph AZ1
EC2_1 --> Aurora_Writer
end
subgraph AZ2
EC2_2 --> Aurora_Writer
Aurora_Writer --> Aurora_Reader
end
end
EC2_1 & EC2_2 --> CloudWatch
Key Components:
- ALB (Application Load Balancer): Distributes HTTP/HTTPS traffic across multiple EC2 instances
- Multi-AZ Configuration: Resources distributed across multiple Availability Zones
- Amazon Aurora: High-performance, highly available RDBMS
- CloudWatch: Monitoring and alerting
Regions and Availability Zones (AZ)
- Region: Geographically separated groups of AWS data centers (Tokyo, Sydney, Virginia, etc.)
- Availability Zone (AZ): Independent data centers within each region
- Physically separated to localize the impact of disasters
- Connected by low-latency, high-speed networks
- Using at least 2 AZs ensures high availability
ALB Components
- Load Balancer: The endpoint serving as the entry point for traffic
- Listener: Accepts requests on specific ports and protocols
- Rules: Determine which target group to forward requests to
- Target Group: A collection of targets such as EC2 instances or containers
Amazon Aurora
Amazon Aurora is a high-performance, highly available relational database compatible with MySQL and PostgreSQL.
Features:
- Up to 5x faster than standard MySQL and 3x faster than PostgreSQL
- Automatic storage expansion (up to 128TB)
- Supports up to 15 read replicas
- Continuous backup and point-in-time recovery
- High availability through Multi-AZ deployment
Aurora Components
- DB Cluster: The entire Aurora database environment
- Primary Instance: An instance supporting both reads and writes
- Read Replica: Read-only instances (for improved scalability and availability)
- Cluster Endpoint: Endpoint for connecting to the primary instance
- Reader Endpoint: Endpoint for connecting to read replicas
DB Subnet Group
When creating an Aurora DB cluster, you must specify a subnet group spanning at least 2 Availability Zones to ensure high availability.
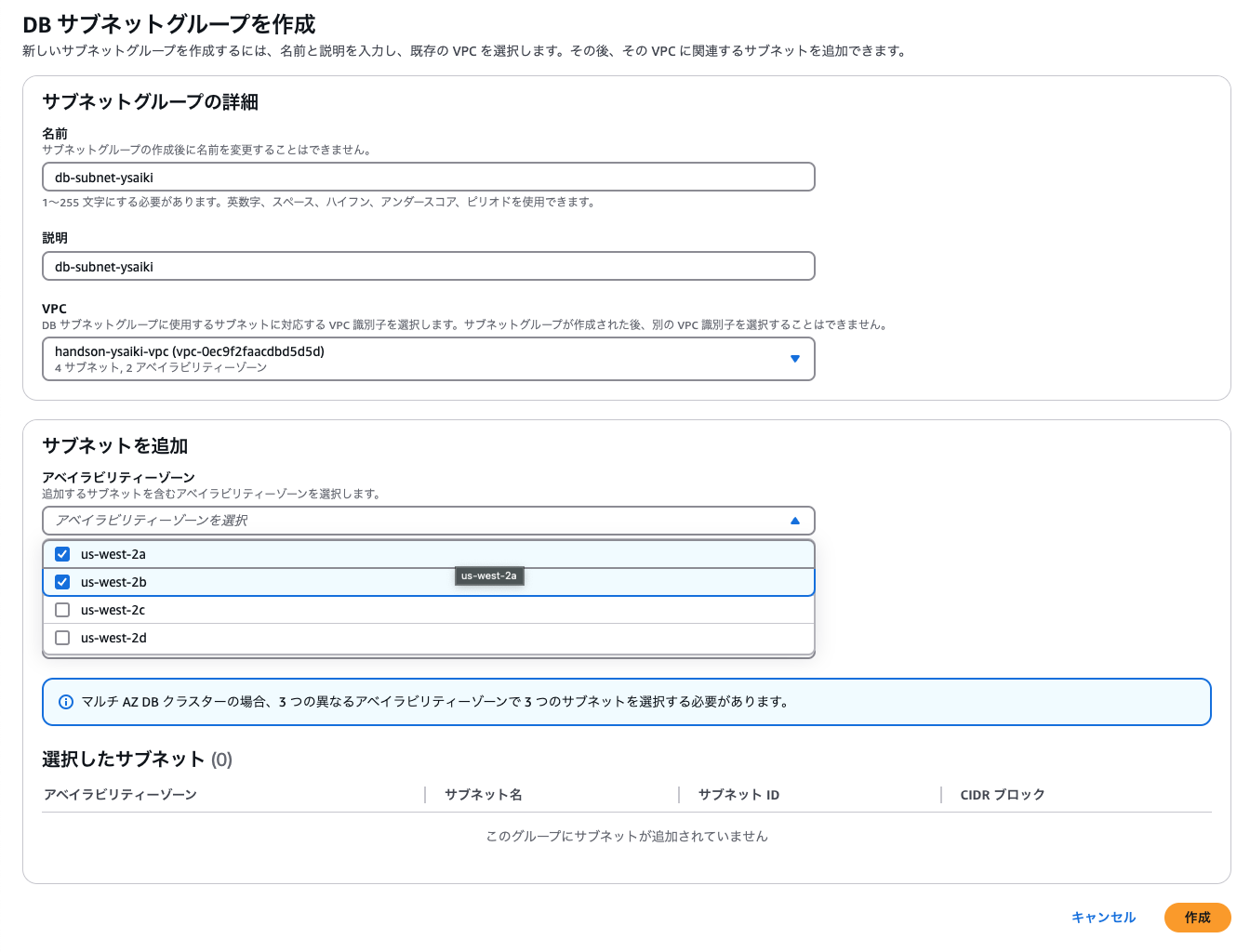
Building Container Environments
Amazon ECS (Elastic Container Service)
Amazon ECS is a fully managed container orchestration service that makes it easy to run and manage containerized applications.
ECS Key Components:
- Cluster: A logical group for running containers
- Task Definition: Container configuration (image, CPU/memory allocation, port mapping, etc.)
- Task: An instance of a task definition (a running container)
- Service: Manages task execution and maintenance
AWS Fargate
Fargate is a compute engine for running ECS or EKS containers in a serverless manner.
Fargate Features:
- No EC2 instance management required
- Precise resource specification per container
- Pay only for resources used
- Security integrated with VPC
Integration Benefits:
- ALB automatically detects dynamic addition/removal of containers
- Automatic detection and exclusion of unhealthy containers through health checks
- Traffic distribution across multiple services via path-based routing
System for the 1 Million+ Users Phase
For even larger scale, more advanced architecture is needed.
Static Content Offloading
- High-speed delivery of static content using CloudFront + S3
- Reduced origin server load and latency
Read Load Distribution
- Adding Aurora read replicas
- Introducing in-memory caching with ElastiCache
Auto Scaling
- Automatically increase/decrease EC2 instances based on demand
- Leveraging target tracking scaling policies
Microservices Architecture
- Splitting into independent services by function
- Managing inter-service communication using API Gateway